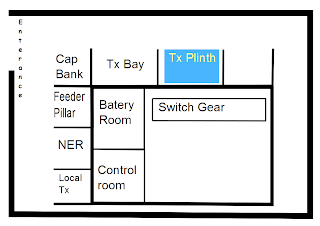
Sub-station categories
Transmission Main Intake (Pencawang Masuk Utama-PMU)
View from the front of PMU Sebarang Jaya, Seberang Perai,Penang.
Transmission Main Intake is the interconnection point of 132kV or 275kV to the distribution network. The standard transmission capacity and voltage transformation provided at the PMU are as follows:-
- 132/33kV, 2 x 90 MVA
- 132 /22kV, 2 x 60 MVA
- 132 /11 kV, 2 x 30 MVA
Main Distribution Sub-station (Pencawang Pembahagian Utama- PPU)
View from the front of PMU Pulau Tikus,Penang.
Main Distribution Sub-station is normally applicable to 33kV for interconnecting 33kV networks with 11 kV networks. It provides capacity injection into 11 kV network through a standardized transformation of 33/11 kV.
Main Switching Station (Stesyen Suis Utama- SSU)
View from the front of SSU Seagate.
SSU at 33kV, 22kV and 11 kV are established to serve the following function:-
1. To supply a dedicated bulk consumer ( 33kV, 22kV, 11 kV)
2. To provide bulk capacity injection or transfer from a PMU/PPU to a load center for further localized distribution.
Distribution Substation (Pencawang Elektrik – P/E)
Side view of P/E Komtar Telekom Exchange
Distribution sub-stations are capacity injection points from 11 kV, 22kV and sometimes 33kV systems to the low voltage network (415V, 240V). Typical capacity ratings are 1000kVA, 750kVA, 500kVA and 300kVA.
Conventional substation designs are of indoor type (equipment housed in a permanent building) and out-door type (ground-mounted or pole-mounted). Standardized M & E design of 11/. 433kV sub-station is available at TNB offices. Compact substation (11 /. 415kV) has limited application and is to be strictly applied in selective situations under the following circumstances:-
§ System reinforcement projects for highly built-up areas where substation land is difficult to acquire.
§ Any request to use compact substation for dedicated supply to a single or limited group of low voltage consumers is subject to TNB approval in accordance to site constraints situation, and to be considered as ‘special feature design schemes’.